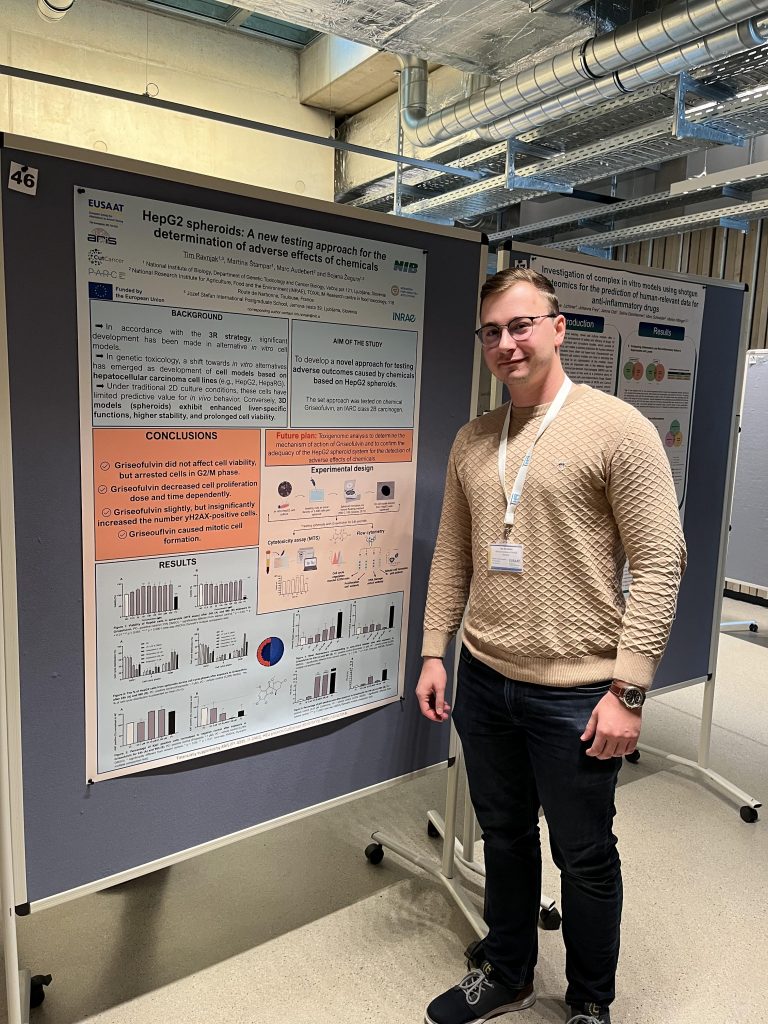
Tim Ravnjak, PhD student from NIB, attended EUSAAT 2024 congress in Linz, Austria and presented his work, titled: HepG2 spheroids: a new testing approach for the determination of adverse effects of chemicals as a poster.
Abstract:
RAVNJAK, Tim, ŠTAMPAR, Martina, AUDEBERT, Marc, ŽEGURA, Bojana. HepG2 spheroids : a new testing approach for the determination of adverse effects of chemicals. V: EUSAAT 2024 : ALTEX proceedings : 24th the European Congress on 3RS, Linz/Austria, September 18-20, 2024. 24th the European Congress on 3RS, Linz/Austria, September 18-20, 2024. Kuesnacht: Springer, 2024. p. 56. Altex proceedings (Internet), Vol. 12, no. 2. ISSN 2194-0479.
In accordance with the 3R (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement) strategy proposed by EU REACH legislation, significant advances have been made in the development of alternative in vitro models to minimize in vivo animal testing. In genetic toxicology, a shift towards in vitro alternatives has emerged with the development of cell models based on hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (e.g., HepG2, HepaRG). However, under traditional 2D culture conditions, these cells have limited predictive value for in vivo behavior. Conversely, 3D models (spheroids) exhibit enhanced liver-specific functions, higher stability, and prolonged cell viability. We aimed to develop a new approach for testing adverse outcomes caused by chemicals, based on HepG2 spheroids grown under static conditions. Three-day old spheroids were exposed to a carcinogen griseofulvin (GF; 2, 20, 200 µM) for 24 and 96-hours and then evaluated for cell viability (MTS), cell cycle distribution (Hoechst 33258), proliferation (Ki67), DNA double strand break (gH2AX) induction and mitotic cell formation (pH3+), coupled with toxicogenomic analyses. Results showed that GF did not affect cell viability, but arrested cells in the G2/M phase. Proliferation increased after 24h exposure however it decreased dose-dependently after 96h. An increase in gH2AX-positive cells was observed after 24h, and mitotic cell formation after 24h and 96h. Toxicogenomic data align with flow cytometry findings. To conclude, this study demonstrates the utility of HepG2 spheroid model in assessing the (geno)toxic effects of chemicals and is a step forward in applying the 3R strategy.