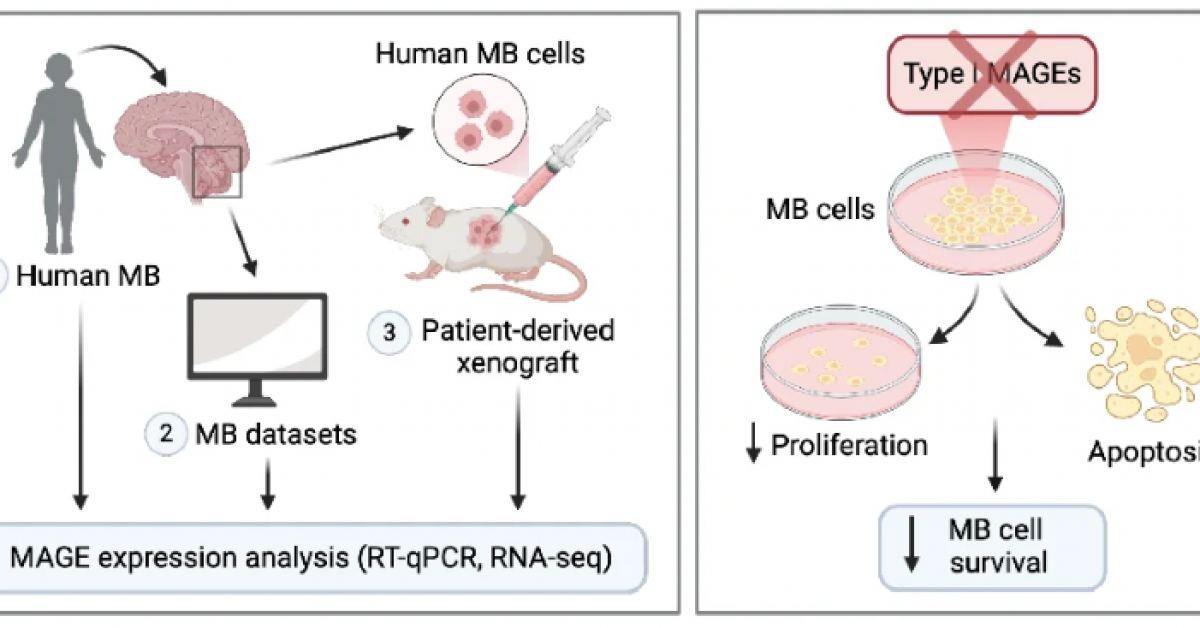
Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most malignant childhood brain cancer. Group 3 MB (G3 MB) subtype accounts for about 25% of MB and is associated with the worst outcomes. Herein, we report that more than half of G3 MB tumors express melanoma antigens (MAGEs), which are potential prognostic and therapeutic markers. MAGEs are cancer-testis antigens, aberrantly expressed in several adult cancers, and associated with poorer prognosis and therapy resistance; however, their role in pediatric cancers is mostly unknown. This study aimed to determine whether MAGEs are activated and important in pediatric MB. We obtained formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor samples of 34 patients, collected between 2008 and 2015 at the Children’s Medical Center in Dallas and applied our validated reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) assay to measure the expression of 23 MAGE genes. To validate our data, we analyzed published datasets from pediatric MB tumors and patient-derived orthotopic xenografts, totaling 949 patients. Our RT-qPCR analysis suggested that MAGEs were expressed in G3/4MB. Further mining of bulk and single-cell RNA-sequencing datasets confirmed that 50–75% of G3 tumors activate several MAGEs. Intriguingly, single-cell data analysis showed that MAGEs are expressed in distinct subsets of cells in MAGE-positive tumors and are not activated in mouse genetic models, suggesting they contribute to the tumor heterogeneity and species-specificity of G3 MB. We then examined how MAGE expression affects the growth and oncogenic potential by CRISPR-Cas9- and siRNA-mediated gene depletion. Depletion of MAGEAs, -B2, and -Cs altered cell survival, viability, and clonogenic growth due to decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis of MAGE-positive MB cells. These findings suggested that targeting MAGEs could represent a viable therapeutic strategy for G3 MB. A deeper understanding of MAGE regulation and function is warranted and could aid in improving prognostic and therapeutic approaches for this poorly characterized subgroup of pediatric brain tumors.
15.10.2025
Melanoma antigens in pediatric medulloblastoma contribute to tumor heterogeneity and species-specificity of group 3 tumors